Calcific tendonitis, a painful musculoskeletal condition that predominantly affects the shoulders, results from the build-up of calcium deposits within the tendons. The accumulation often occurs over time, leading to inflammation and discomfort that can impact a person’s ability to carry out daily activities. This condition may progress gradually and is often related to age, with middle-aged and older adults being the most susceptible demographic.
In the UK, calcific tendonitis is a notable health concern, contributing significantly to the overall cases of shoulder pain reported in adults. Though comprehensive national statistics on the condition’s prevalence are not readily available, anecdotal evidence and clinical encounters suggest a substantial number of affected individuals.
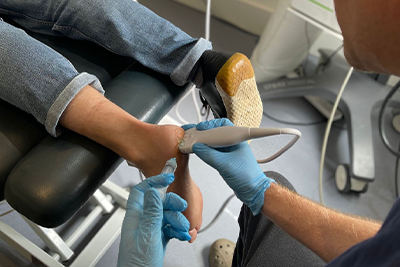
One emerging treatment modality for calcific tendonitis that has been gaining increased attention over the past few years is Shockwave Therapy. This non-invasive treatment technique uses high-energy acoustic waves to stimulate healing and reduce pain, representing a potential alternative to traditional approaches like physiotherapy or invasive surgery.
Understanding Calcific Tendonitis
Calcific tendonitis is a complex condition, with its pathophysiology rooted in the accumulation of calcium deposits within the tendons. These deposits are typically concentrated in the shoulder’s rotator cuff tendons, although they can occur in other areas of the body. The exact cause of this calcium build-up is unknown, but it’s thought to be linked to ageing, tendon damage or wear, or metabolic diseases.
The process begins with a pre-calcification stage, where the tendon’s cellular changes occur. It is followed by the calcific stage, where calcium deposits form and mature over time. Eventually, the body attempts to reabsorb these calcium deposits in a process known as the post-calcific stage. This phase often leads to an inflammatory response, resulting in the onset of pain and discomfort that characterises calcific tendonitis.
The symptoms of calcific tendonitis vary from person to person. Still, they can include chronic pain that worsens with movement, a noticeable hard lump in the tendon area, and reduced range of motion. This discomfort can significantly impact the quality of life, as it often impedes routine tasks like dressing, driving, or sleeping.
Conventional calcific tendonitis treatments aim to manage symptoms and dissolve calcium deposits. They include pain management strategies such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), physiotherapy for improved mobility, and corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation. In some instances, shockwave therapy is used to break up the calcium deposits, promoting reabsorption by the body. In severe cases where other treatments are ineffective, surgical intervention might be necessary to remove the calcium deposits directly.
A Closer Look at Shockwave Therapy
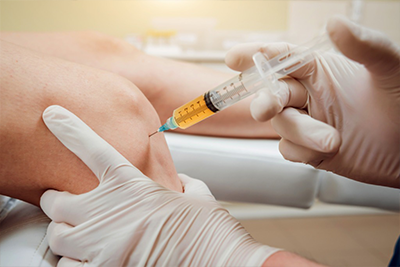
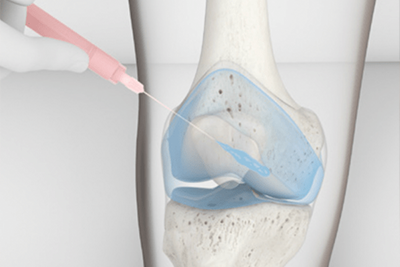
Shockwave therapy, also known as Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT), is a non-invasive treatment modality that employs high-energy acoustic waves to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes. It delivers focused shockwaves to the target area, which is the affected tendon in calcific tendonitis. These shockwaves induce a controlled inflammatory response that can help break up the calcium deposits, thereby accelerating the healing process.
Shockwave therapy has been applied in various fields of medicine over the past few decades. It was initially used to dissolve kidney stones, but its potential in treating musculoskeletal conditions was soon recognised. Today, it is used to treat conditions such as plantar fasciitis, tennis elbow, Achilles tendinopathy, and calcific tendonitis.
For calcific tendonitis, shockwave therapy targets the calcium deposits within the tendons. The high-energy waves applied to the site can help break down these deposits, which are reabsorbed by the body. This process reduces inflammation and, subsequently, the pain experienced by the patient.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), the body that sets guidelines for health practice in the UK, has recognised the potential of shockwave therapy in treating musculoskeletal disorders. Their guidelines have deemed shockwave therapy safe for use, provided a trained professional carries it out. However, NICE also mentions that the evidence of its efficacy needs to be more consistent, indicating a need for more comprehensive studies. They recommend its use when other treatment options have not provided satisfactory results or are unsuitable for the patient. The ultimate decision to use shockwave therapy should involve a detailed discussion between the healthcare provider and the patient, considering the patient’s overall health condition, personal preference, and specific cases of calcific tendonitis.
Effectiveness of Shockwave Therapy for Calcific Tendonitis
The effectiveness of shockwave therapy for calcific tendonitis has been the subject of considerable research and clinical studies, and while the overall picture is positive, findings do vary.
Several studies have shown promising results. For example, a 2017 systematic review and meta-analysis in the American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation found that shockwave therapy was significantly more effective than conventional treatments in both the short and long term for reducing pain and improving function in patients with calcific tendonitis.
Moreover, a research study in the Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research in 2018 discovered that, in a cohort of 80 patients with shoulder calcific tendonitis, those treated with shockwave therapy demonstrated significant improvements in shoulder function and reductions in pain compared to those treated with conventional methods. This study also noted that most patients experienced complete resolution of their calcium deposits after shockwave therapy.
However, it’s worth noting that the results of these studies could be more uniformly positive. Some studies suggest that the success of shockwave therapy might depend on the size and location of the calcium deposits, with smaller and more superficial deposits responding better to the treatment.
In terms of patient satisfaction and recovery times, these appear to be generally positive. Patients often appreciate the non-invasive nature of shockwave therapy, and the recovery time is usually shorter than surgical interventions. That said, the total recovery time can depend on various factors, such as the severity of the calcific tendonitis and the patient’s overall health.
Specific to the UK, a 2015 study published in the European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology evaluated the effects of shockwave therapy in 60 patients with shoulder calcific tendonitis across multiple clinical centres. The study found a significant reduction in pain and improved shoulder function, supporting shockwave therapy as a treatment option.
Risks and Benefits of Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave therapy offers several potential benefits for patients suffering from calcific tendonitis. Firstly, it provides a non-invasive treatment option, thus avoiding the risks associated with surgery and prolonged recovery periods. The therapy has effectively reduced pain in several cases, thereby improving patients’ quality of life and enabling them to resume daily activities with less discomfort.
Furthermore, shockwave therapy often results in improved mobility by breaking down the calcific deposits, reducing inflammation, and stimulating the healing process within the tendons. This enhanced range of motion can further improve patients’ quality of life and assist in their overall recovery.
However, like all medical interventions, shockwave therapy is not without potential risks and side effects. According to the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), side effects can include pain during and after treatment, skin reddening, bruising, and swelling. In rare instances, there might be a risk of tendon damage. However, these side effects are usually temporary and often resolve within a week following treatment.
Contraindications for shockwave therapy include pregnancy, malignancies, infections, or disorders related to blood clotting. Additionally, shockwave therapy should not be applied over air-filled tissues or organs or directly over growth plates in younger patients. As always, shockwave therapy should result from a detailed discussion between the patient and the healthcare provider, considering individual health status and weighing potential benefits against potential risks.
Testimonials
Providing a human touch to the scientific discussion, patient testimonials, and case studies can offer a valuable perspective on the real-life impact of shockwave therapy for calcific tendonitis. They provide a unique insight into the patient’s experiences, shedding light on their journey from diagnosis to recovery and shockwave therapy’s role in this process.
John, a 45-year-old avid tennis player from Ashford. John was diagnosed with calcific tendonitis after experiencing chronic shoulder pain. His discomfort eventually started interfering with his tennis games and daily life. He tried conventional treatments, including painkillers and physiotherapy, but found little relief. John then opted for shockwave therapy. After several treatments, he noticed a significant reduction in pain and gradually returned to playing tennis without discomfort.
Sarah, a 55-year-old office worker from London, was diagnosed with calcific tendonitis. The constant pain in her shoulder affected her ability to work effectively and significantly impacted her quality of life. After undergoing shockwave therapy, Sarah experienced a substantial reduction in pain and improvement in shoulder mobility, allowing her to return to her regular work routine.
Your Health Matters to Us
At Vale Health Clinic, we understand that dealing with a condition like calcific tendonitis can be challenging. If you or a loved one are struggling with this condition, remember there are effective treatments available that could make a significant difference in your life.
Our team is here to support you in your journey towards better health. We’re happy to discuss shockwave therapy’s potential benefits and risks for calcific tendonitis alongside other treatment options.
So, why wait? Reach out to us today to schedule a consultation. Let us guide you towards the most suitable treatment option for your unique needs and get you back to living life to the fullest.
Related Articles
- Golfer’s Elbow: Causes, Symptoms, and Shockwave Therapy Treatment
- Types of Tendonitis that Shockwave Therapy Can Treat
- How Does Shockwave Therapy Work on Tendons
- Can Shockwave Therapy Help With Musculoskeletal Problems
- Shockwave Therapy For Running Injuries